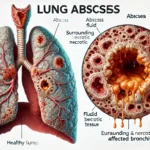
Lung Abscess: How Does a Hidden Infection Lead to a Collapsed Defense?
A lung abscess is a localized infection in the lung tissue, resulting in a cavity filled with pus and necrotic debris. This serious condition often arises as a complication of aspiration pneumonia or other infections. If not promptly treated, a…











